Have you ever noticed an itchy, peeling sensation between your toes that just won’t go away? Or maybe the skin on your feet feels unusually dry, cracked, or irritated—even when you’re keeping clean? These could be more than just harmless dryness or a reaction to tight shoes.
In fact, these are some of the most common early signs of a condition many people overlook until it becomes uncomfortable or even painful: athlete’s foot. Despite its name, this foot condition doesn’t only affect athletes—it can happen to anyone.
So how do you know if it’s just dry skin… or something more? Let’s explore the warning signs, treatment options, and how you can stop athlete’s foot before it spreads.
What Is Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot, also known medically as tinea pedis, is a fungal infection of the skin on the feet. It thrives in warm, moist environments, which makes locker rooms, communal showers, and sweaty shoes ideal places for the fungus to grow.
It typically starts between the toes and may spread to other areas of the foot. The condition is contagious and can spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, towels, or shoes.
What Are the Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot?
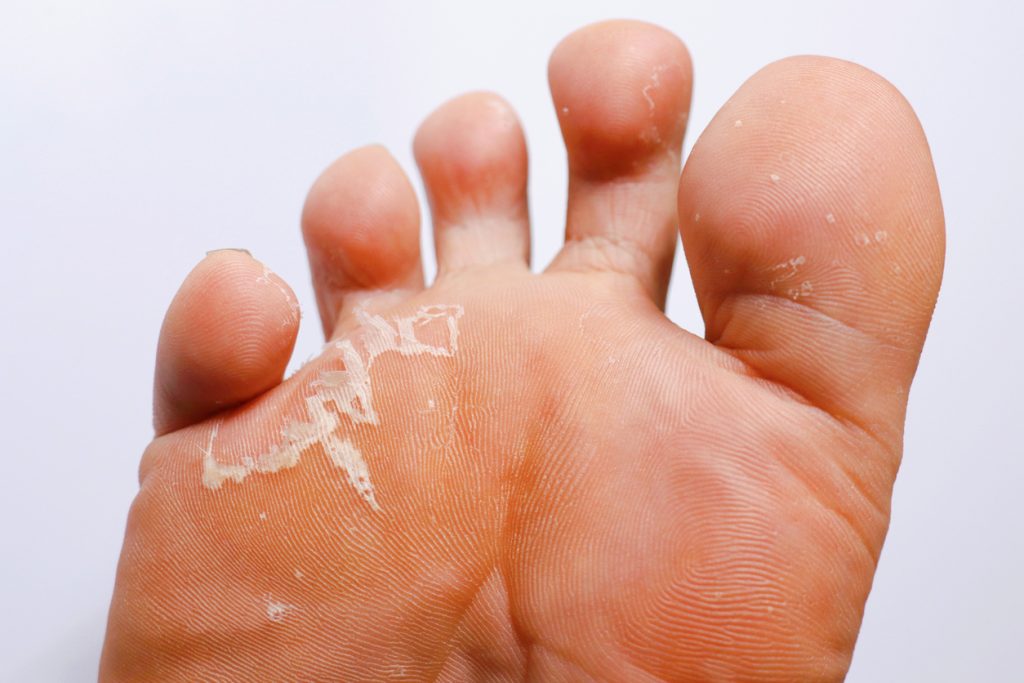
Common signs and symptoms of athlete’s foot include:
-
Itching or burning between the toes or on the soles of the feet
-
Redness or scaling of the skin
-
Dry, flaky skin especially around the heels or edges of the feet
-
Cracking or peeling skin, particularly in the toe web spaces
-
In some cases, small blisters or open sores may develop
-
An unpleasant odor from the feet
It’s important to recognize these symptoms early to begin treatment before the infection worsens or spreads.
How Do You Treat Athlete’s Foot?
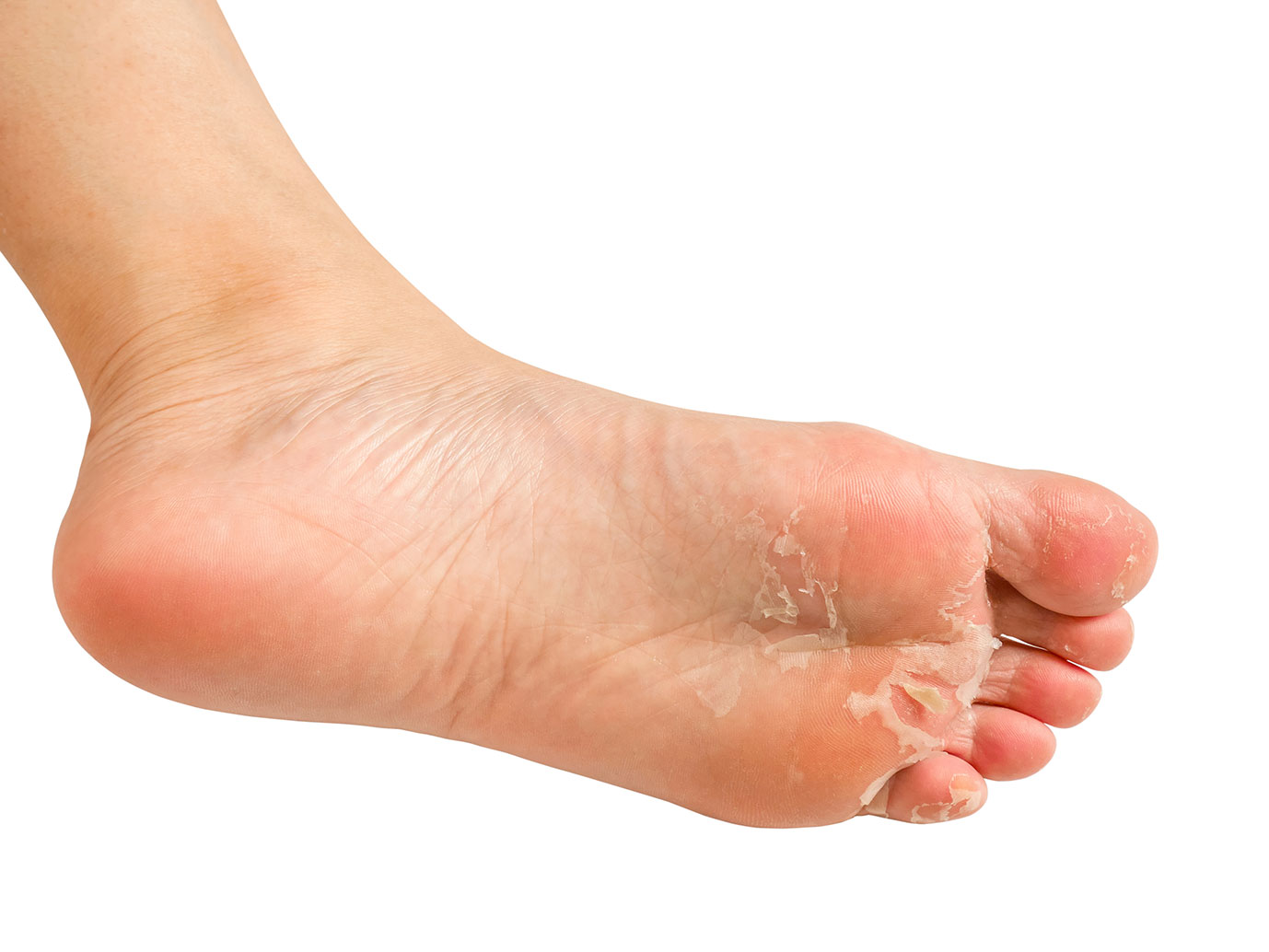
Treatment for athlete’s foot typically involves topical antifungal medications. These are available over-the-counter (OTC) or by prescription, depending on the severity of the infection.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Many mild cases can be treated effectively with antifungal creams, ointments, sprays, gels, or powders. These products often contain active ingredients such as:
-
Clotrimazole
-
Miconazole
-
Tolnaftate
-
Terbinafine
These treatments are generally applied once or twice a day for 2 to 4 weeks. Be sure to read and follow the product instructions carefully, and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve sooner.
Prescription Medications
In more persistent or widespread cases, healthcare providers may recommend oral antifungal medications, such as:
-
Fluconazole
-
Itraconazole
-
Terbinafine (oral form)
These medications may be prescribed if topical treatments haven’t worked or if the infection has spread to the toenails or other parts of the body.
Managing Athlete’s Foot at Home
_996x996a.png)
While undergoing treatment, practicing good hygiene is essential to prevent reinfection and stop the fungus from spreading. Here are some helpful tips:
-
Keep your feet clean and dry, especially between the toes
-
Change socks daily, or more often if your feet sweat
-
Wear breathable shoes and alternate pairs to allow drying time
-
Use a separate towel for your feet and wash it regularly
-
Avoid walking barefoot in communal showers, locker rooms, and around pools
-
Do not scratch affected areas, as this may spread the infection to your hands or other body parts
If possible, give your feet time to “breathe” by not wearing socks and shoes at home.
How Long Does It Take to See Improvement?
With proper care and consistent use of antifungal medication, most people see significant improvement within 1 to 8 weeks. Itchiness and redness may begin to fade within a few days of starting treatment, but it’s important to complete the full course, even if the skin looks healed.
Stopping treatment too soon may cause the infection to return—and it could be more difficult to eliminate the second time.
What Happens If Athlete’s Foot Is Left Untreated?
If not treated, athlete’s foot can become more severe and spread beyond the feet. Potential complications include:
Moccasin-Type Athlete’s Foot
This form affects the soles, heels, and sides of the feet, leading to dry, thickened, scaly skin. It can be persistent and more resistant to basic treatments.
Nail Involvement
The infection can spread to the toenails, resulting in thick, discolored, or brittle nails. Nail infections often require longer treatment with oral medications.
Hand Involvement
When scratched or touched, the infection may spread to the hands—usually on the palms or between the fingers—creating similar itchy, dry, or scaly patches.
Groin Area Infections
The fungus can also spread to the groin, resulting in a condition commonly known as jock itch. This happens when the same towel or hands touch both areas, especially after bathing or exercising.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
You should consult a healthcare provider if:
-
The rash is not improving after 2 weeks of treatment
-
The condition appears to be getting worse or spreading
-
You have diabetes or a weakened immune system
-
You develop blisters, open sores, or signs of infection (pus, increased redness, swelling)
Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications and discomfort.
Final Thoughts
Athlete’s foot is a common and manageable condition. With proper hygiene, early treatment, and awareness of symptoms, it can be controlled and often eliminated entirely. The key is to act early, follow your treatment plan consistently, and take preventive steps to avoid recurrence.
If you suspect you have athlete’s foot, over-the-counter options are a good place to start—but don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional if the infection persists.
