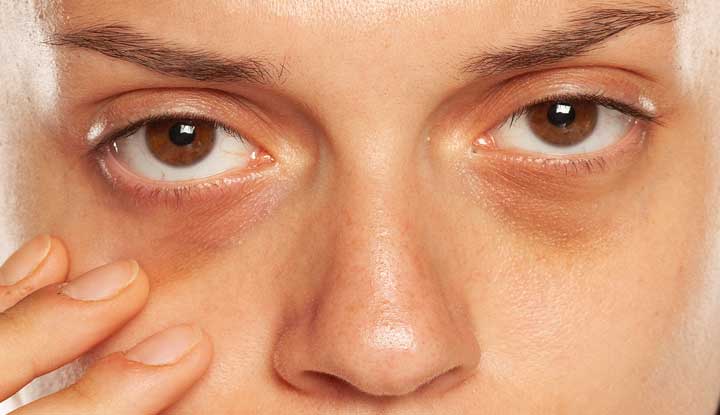
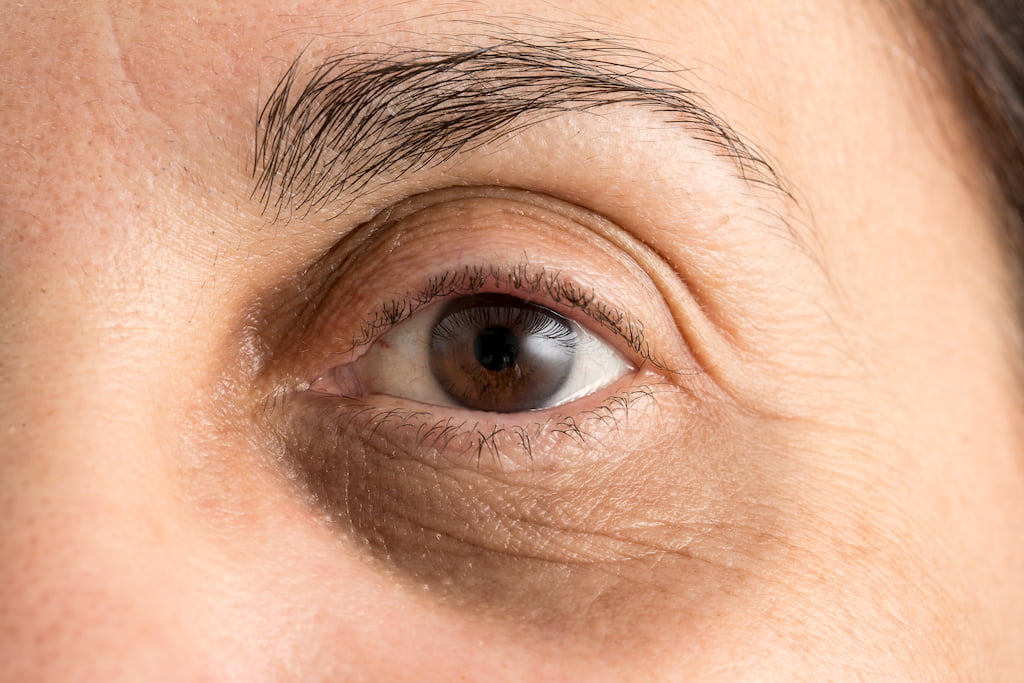
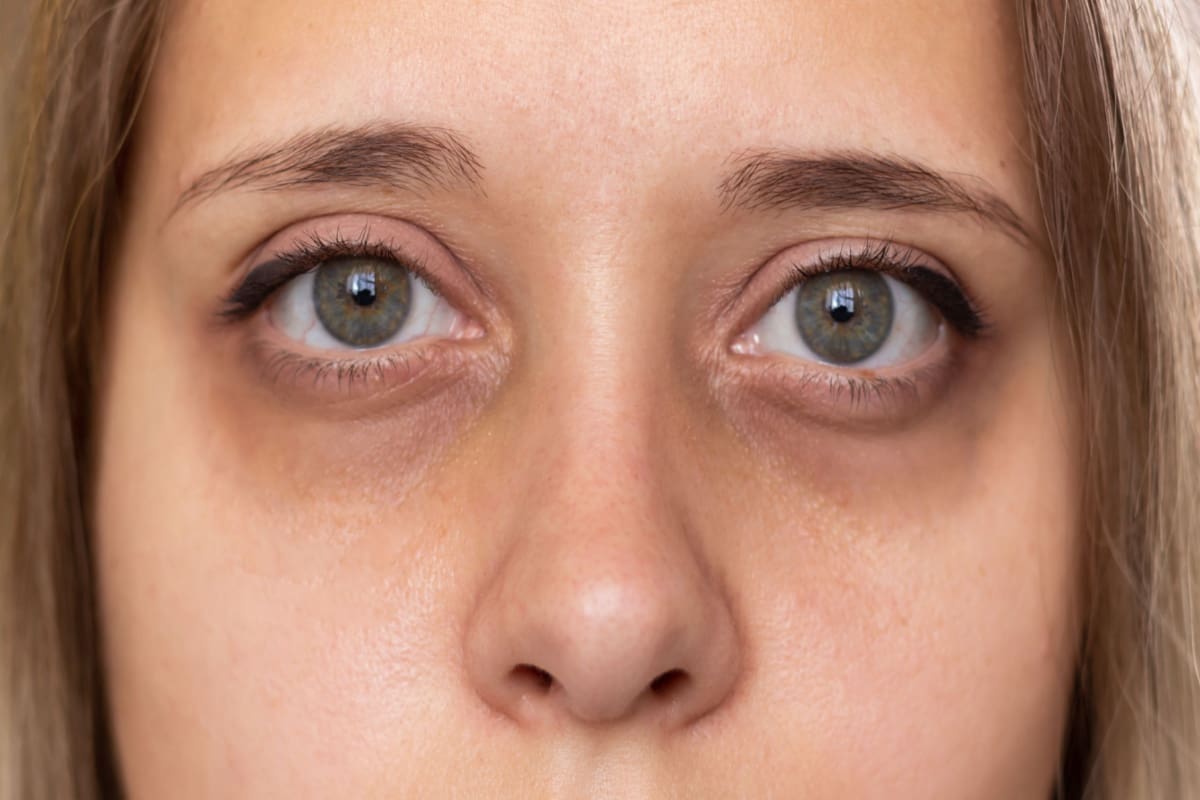
Dark circles and puffiness under the eyes are common cosmetic concerns that affect people of all ages. While they are often linked to fatigue or aging, persistent or worsening discoloration in this area can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes and knowing when to seek medical advice can help you address the problem effectively.
What Are Dark Circles?
Dark circles refer to areas of skin under the lower eyelids that appear darker than the surrounding facial skin. They can be accompanied by puffiness or swelling, often called “under-eye bags.” Although they are not usually a medical concern, their appearance can affect self-confidence and sometimes indicate health-related issues.
Common Causes of Dark Circles
Dark circles can result from various factors, many of which are temporary or manageable. Here are the most frequent causes:
1. Lack of Sleep
While research has not fully established a direct cause-and-effect relationship between poor sleep and under-eye darkening, insufficient rest can make the area appear more pronounced. A lack of sleep may cause the skin to appear pale, making blood vessels under the skin more visible.
2. Genetics
Hereditary factors play a significant role. Some individuals naturally have more pigment or thinner skin under their eyes due to genetic traits. If close family members have dark circles, you may be more likely to develop them.
3. Sun Exposure and Hyperpigmentation
Excessive sun exposure can increase melanin production, leading to skin darkening under the eyes. This effect can be amplified by genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, or allergic reactions. The condition, known as periorbital hyperpigmentation, is common and may affect emotional well-being.
4. Allergies and Inflammation
Allergic reactions trigger the release of histamines, which can cause swelling, itchiness, and dilation of blood vessels. This can result in puffiness and discoloration under the eyes. Chronic allergies or sinus issues can make these symptoms more persistent.
5. Skin Conditions (Dermatitis)
Eczema and contact dermatitis can damage the delicate skin around the eyes, making underlying blood vessels more visible. Repeated rubbing or scratching due to irritation can worsen the discoloration.
6. Dehydration
Inadequate water intake can make the skin under the eyes look dull, sunken, and more shadowed. Staying hydrated helps maintain skin elasticity and brightness.
7. Aging and Skin Thinning
Over time, skin loses collagen and becomes thinner. This natural aging process makes the blood vessels beneath the eyes more noticeable. Gravity also contributes to the sagging of skin, which can increase shadowing.
8. Lifestyle Factors
Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, stress, and poor diet can all contribute to dark circles by affecting skin health, hydration, and circulation.

When to See a Doctor
Most dark circles are harmless, but in some cases, they may signal underlying health concerns. Seek medical advice if you notice:
-
Persistent dark circles despite adequate sleep, hydration, and skincare
-
Sudden or severe discoloration without clear cause
-
Dark circles accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or swelling in other parts of the body
Possible Medical Causes
1. Poor Blood Circulation
Sluggish circulation can cause blood to pool under the eyes, resulting in a darker appearance. Conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels, as well as a sedentary lifestyle, may contribute to this problem.
2. Food Sensitivities
Certain food intolerances can cause inflammation, which may appear as puffiness or discoloration under the eyes. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can help reduce symptoms.
3. Iron Deficiency (Anemia)
Low iron levels can reduce oxygen delivery to the skin, causing it to look dull and discolored. Symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or feeling cold may accompany dark circles in cases of anemia.
Tips for Reducing Dark Circles
While not all causes are preventable, lifestyle adjustments and home remedies can help minimize their appearance.
1. Improve Sleep Quality
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful environment can make a noticeable difference.
2. Protect Skin from Sun Damage
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, wear sunglasses, and avoid excessive sun exposure to reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation.
3. Stay Hydrated
Drink enough water throughout the day to keep skin hydrated and healthy-looking.
4. Manage Allergies
Consult a healthcare provider for allergy management strategies, including medications or environmental adjustments.
5. Adopt a Healthy Diet
Include iron-rich foods, fresh fruits, vegetables, and protein in your meals. Limit processed foods, excessive sugar, and salt.
6. Use Cold Compresses
Applying a cold compress or chilled cucumber slices can temporarily reduce puffiness and improve circulation.
7. Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol
Both habits can accelerate skin aging, reduce collagen production, and worsen discoloration.
Cosmetic and Medical Treatments
If home remedies are insufficient, professional treatments may help:
-
Topical creams containing retinoids, vitamin C, or caffeine can brighten skin and improve texture.
-
Chemical peels can reduce pigmentation under the eyes.
-
Laser therapy targets pigmentation and stimulates collagen production.
-
Fillers can address volume loss and reduce shadowing.
-
Microneedling promotes skin rejuvenation.
Always consult a licensed dermatologist or healthcare provider before beginning any medical or cosmetic treatment.
Final Thoughts
Dark circles under the eyes are common and often harmless, but they can sometimes signal underlying health conditions. By identifying the cause—whether it’s lifestyle-related, genetic, or medical—you can choose the most effective solution. Good skincare habits, a balanced lifestyle, and timely medical advice can help restore a refreshed and healthy appearance.